LASER CUTTING
1. Learn how to keep safety
Selection and use of laser protective glasses:
Make sure to use protective glasses that are appropriate for the type and power of the laser, usually labeled with the type of laser and level of protection applicable.
And ensure that the protective glasses are not damaged or worn during use, and replace the damaged protective glasses in time.
Inspection and use of equipment safety features:
Test the function of the emergency stop button before each operation. These buttons are usually located in an easily accessible part of the operating area to quickly stop the device in case of an emergency.
Ensure that the laser cutting equipment's protective cover is intact and properly installed. The shield can effectively reduce the direct exposure of laser radiation to the operator.
Security Settings for the operation area:
Place the laser cutting equipment on a stable workbench and ensure that the equipment is level to avoid accidents caused by shaking or tilting the equipment.
Set up an appropriate working space in the operation area and ensure that there is no debris or obstacles around to prevent the operator from tripping or bumping into the equipment.
Waste disposal and soot control:
Use effective exhaust system and smoke extraction equipment to quickly discharge smoke and harmful gases from the operating area to keep the air fresh and the health and safety of the operator.
Clean equipment and operating areas regularly, especially where waste and by-products accumulate, to avoid the risk of dust or carbon buildup.
Emergency response and preparedness measures:
Place clearly marked first aid kits and eye douches near the operation area and ensure that all operators know their location and how to use them.
Develop and practice an emergency evacuation plan, including how to safely shut down equipment and leave the operation area.

2. Learn different kind of material which can be manufacture by laser cutter
Metal materials:
Machine Type: Fiber Laser Cutting machine:
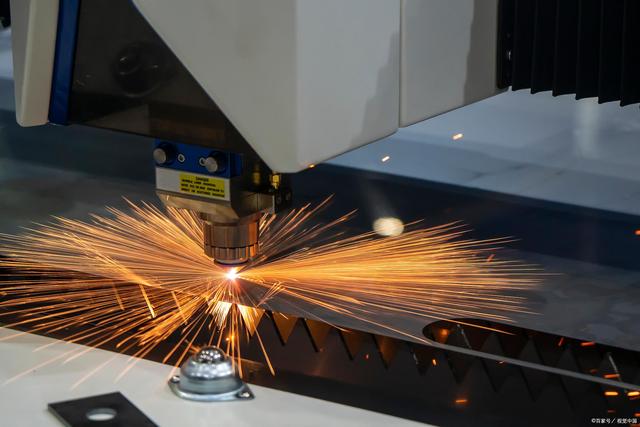

Fiber laser cutting machine uses fiber as the medium for laser transmission, and the laser source is usually a high-energy fiber laser.
Fiber laser cutting machines are suitable for thinner sheet metal and higher cutting speed requirements, usually dealing with a thickness of a few millimeters to about 20 millimeters of sheet metal.
They have high cutting accuracy and small cutting width, suitable for detailed and complex cutting tasks.
Steel(Q235) and stainless steel(AISI 304): Laser cutting machine for steel and stainless steel processing is very common, can be used to manufacture a variety of mechanical parts, structural parts, etc.
Aluminum(1050): Aluminum alloy is often used in the aerospace and automotive industries because of its good thermal conductivity and processing properties, and laser cutting is suitable for its processing.
Copper(C11000) and brass(C26000): These conductive materials are widely used in electronics and art manufacturing, and laser cutters can process them efficiently.
Non-metallic materials:
Plastic: Laser cutting for a variety of plastic materials such as propylene, polycarbonate, etc., are suitable for manufacturing models, signs, parts, etc.
Wood and wood products: Wood, MDF panels, etc., are common in the manufacturing of furniture and decorations, and laser cutting machines can perform precise engraving and cutting.
Leather and fabric: Used in the manufacture of clothing, footwear, bags, etc., laser cutting can achieve fine patterns and edge treatment.
Other materials:
Glass and ceramics: Laser cutting machines can process glass and ceramics to a certain extent for making ornaments and crafts.
Paper and fiberboard: Commonly used in the printing and packaging industries, laser cutters can cut and carve efficiently.
CNC manufacture
01.how to keep safety
Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) :
Include safety glasses, ear plugs or muffs (if the device is noisy), gloves, and tight clothing.Additional protective equipment, such as protective boots or helmets, may be required depending on the job.
Equipment inspection and maintenance:
Check equipment before each use to ensure that all safety devices and fasteners are in good condition.
Perform regular equipment maintenance and maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication and replacement of worn parts.
Correct operating procedures:
Use the correct tool and tool path to avoid overly aggressive cutting or unsafe process parameters.
Follow the manufacturer's operating manual and recommendations, especially regarding maximum speed, feed rate and depth of cut.
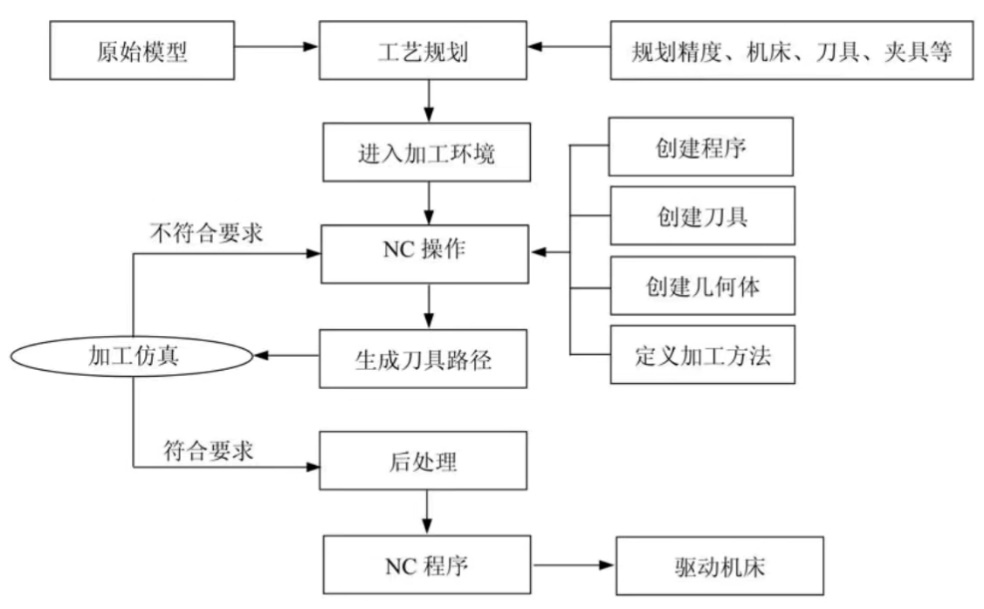
02. CNC in indusrty: machine type, application
CNC Mills:
Applications: For the processing of 2D and 3D shapes, including plane processing, contour processing, hole processing and surface processing. Widely used in metal processing, woodworking and plastic processing and other fields.
Features: The tool can be moved upward in multiple axes according to the preset program to realize the machining of complex parts.
CNC Drills:
Application: It is mainly used for accurate hole machining, including single hole and multi-hole drilling modes. Suitable for metal, plastic and composite material processing.
Features: The position and feed of the bit can be precisely controlled to achieve accurate hole machining requirements.

03.make sure the machine material——Aluminum alloy processing

Features: Aluminum alloy is easy to cut, VMC has good flexibility and high processing speed, suitable for the mass production of small and medium-sized parts.
Applications: aerospace parts, automotive parts, electronic product enclosures.
Advantages: Efficient processing, good surface finish, relatively low equipment cost.
Machine Type: Vertical Machining Center (VMC)
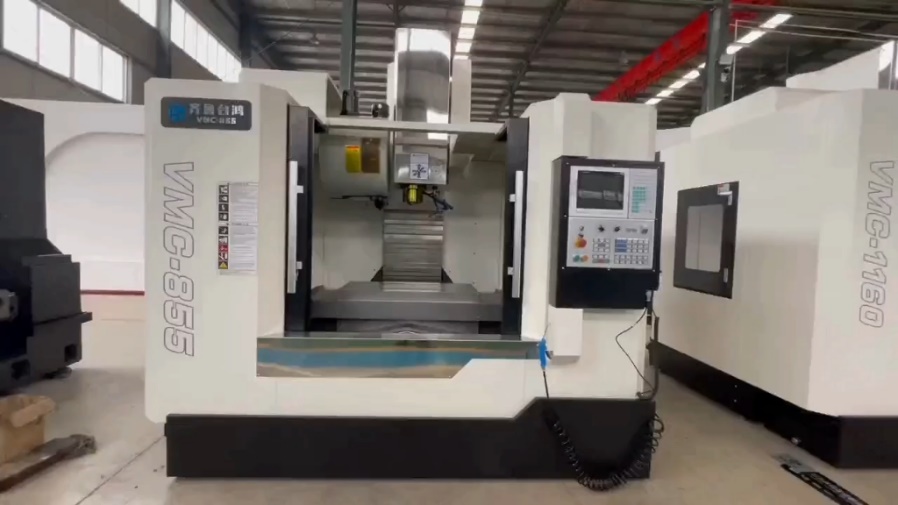

Steps and Tools:
Knife:
Milling cutter: Solid carbide (cemented carbide) tools are usually used, such as single, double or ball end milling cutters.
Drill bit: Carbide drill bit is commonly used, and the choice of the appropriate diameter drill bit can be carried out according to needs.

Cutting parameter setting:
Speed and feed rate: Aluminum alloys can usually be used with higher cutting speeds. Typically, the rotational speed is between 3,000 and 10,000 RPM, depending on the type of tool used and the size of the workpiece.
Depth of cutting: Determine the appropriate depth of cutting according to the specific workpiece and tool diameter. It is usually recommended that the depth of each cut not exceed half of the diameter of the tool.
Cooling and lubrication:
For aluminum alloy processing, cooling and lubrication are very important to prevent tool overheating and extend tool life. Appropriate cutting oil or specialized coolant be used.
Process
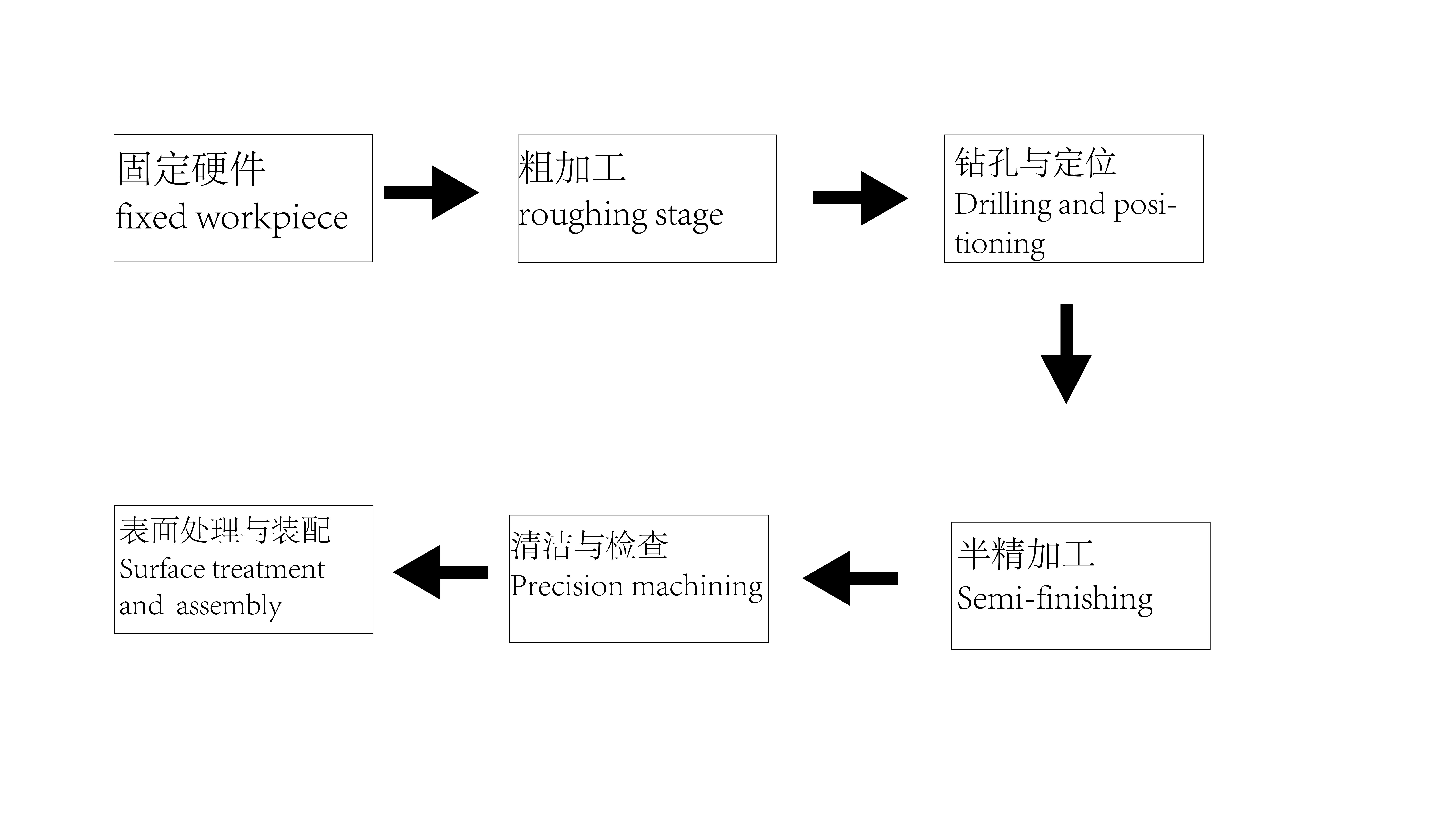
fixed workpiece:
The aluminum alloy workpiece is installed on the work table of the CNC vertical machining center and fixed with the appropriate fixture to ensure the stability and safety of the workpiece.
Roughing stage:
Roughing with a rough milling cutter removes most of the excess aluminum alloy material.Set a high cutting speed and feed rate to remove materials quickly, but make sure that no tools and machines are loaded.
Drilling and positioning:
According to the requirements of the CAD/CAM program, the use of suitable carbide drill bits for hole machining, such as positioning holes, threaded holes, etc.
Ensure that the position and dimensions of each hole are accurate to ensure the accuracy of subsequent processing.
Semi-finishing stage: